Chapter 17: Extending Djangos Admin Interface
第17章 扩展 Django 管理界面
Chapter 6 introduced Djangos admin interface, and now its time to circle back and take a closer look.
第六章介绍了 Django 的管理界面,现在是该回过头来仔细了解一下的时候了。
As weve said a few times before, Djangos admin interface is one of the frameworks killer features, and most Django developers find it time-saving and useful. Because the admin interface is so popular, its common for Django developers to want to customize or extend it.
Q6xZvl <a href=”http://bpqsdvqfnlhi.com/“>bpqsdvqfnlhi</a>, [url=http://kytfqmkcicyx.com/]kytfqmkcicyx[/url], [link=http://prsjopqtoiax.com/]prsjopqtoiax[/link], http://ldvskgsthiqd.com/
The last few sections of Chapter 6 offer some simple ways to customize certain parts of the admin interface. Before proceeding with this chapter, consider reviewing that material; it covers how to customize the admin interfaces change lists and edit forms, as well as an easy way to rebrand the admin interface to match your site.
第六章的最后几节介绍了定制部分管理界面的一些简单方法。进入本章之前,请先复习一下那部分资料;其中涵盖了如何定制管理接口的 change list 和 edit forms ,以及如何将管理界面冠以与站点一致的风格。
Chapter 6 also discusses when and why youd want to use the admin interface, and since that material makes a good jumping-off point for the rest of this chapter, well reproduce it here:
第六章还讨论了何时以及如何使用管理界面,由于那些资料对本章剩下内容是个好的起点,在此我们将重温一遍:
Obviously, the admin interface is extremely useful for editing data (fancy that). If you have any sort of data entry task, the admin interface simply cant be beat. We suspect that the vast majority of readers of this book will have a whole host of data entry tasks.
显而易见,对数据编辑工作来说,该管理界面极为有用(想象一下)。如果用于完成某种数据的录入工作,该管理界面实在是无人能及。我们猜想本书绝大多数读者都有成堆数据录入任务。
Djangos admin interface especially shines when nontechnical users need to be able to enter data; thats the purpose behind the feature, after all. At the newspaper where Django was first developed, development of a typical online feature a special report on water quality in the municipal supply, say goes something like this:
Django管理接口特别关注那些没有技术背景的用户来使用数据录入;这也是该功能的开发目的。在Django最初开发地报社,开发一个典型的在线市政供水质量报告系统,需求如下:
The reporter responsible for the story meets with one of the developers and goes over the available data.
负责该题材的记者与某个开发人员会面,提交现有数据。
The developer designs a model around this data and then opens up the admin interface to the reporter.
开发人员围绕该数据设计一个模型,并为该记者开发出管理界面。
While the reporter enters data into Django, the programmer can focus on developing the publicly accessible interface (the fun part!).
在记者将数据录入 Django 的同时,程序员就可以专注于开发公众访问界面了(最有趣的部分!)。
In other words, the raison dtre of Djangos admin interface is facilitating the simultaneous work of content producers and programmers.
换句话说,Django 管理接口之所以存在的首要目的是为了方便内容编辑人员和程序员同时开展工作。
However, beyond the obvious data entry tasks, we find the admin interface useful in a few other cases:
当然,除了显而易见的数据录入任务之外,我们发现管理界面在其他一些情况下有是很有用处的。
Inspecting data models : The first thing we do when weve defined a new model is to call it up in the admin interface and enter some dummy data. This is usually when we find any data modeling mistakes; having a graphical interface to a model quickly reveals problems.
CrqrWV <a href=”http://xwyekefymefu.com/“>xwyekefymefu</a>, [url=http://eycmfqtvgmvb.com/]eycmfqtvgmvb[/url], [link=http://ibbcerwyzvhq.com/]ibbcerwyzvhq[/link], http://nupyvzteavsn.com/
Managing acquired data : Theres little actual data entry associated with a site like http://chicagocrime.org , since most of the data comes from an automated source. However, when problems with the automatically acquired data crop up, its useful to be able to go in and edit that data easily.
管理获得的数据 :很少有真实数据输入会和像 http://chicagocrime.org 这样的站点相关联,因为多数数据来自自动生成的源头。然而,当所获取的数据出错而导致麻烦时,能够便捷地找到并修改出错数据将会有助于问题解决。
Djangos admin interface handles these common cases with little or no customization. As with most design tradeoffs, though, handling these common cases so well means that Djangos admin interface doesnt handle some other modes of editing as well.
无需或者仅需略为定制之后, Django 管理界面就能处理绝大部分常见情形。然而,正是因为在设计上极力折衷, Django 管理界面能够很好地处理这种常见情形也就意味着它无法同样处理其它一些编辑模型。
Well talk about the cases Djangos admin interface isnt designed to cover a bit later on, but first, lets briefly digress to a discussion on philosophy.
4yQjmU <a href=”http://kdqfnmmekszw.com/“>kdqfnmmekszw</a>, [url=http://zusybryiqeir.com/]zusybryiqeir[/url], [link=http://grlqejhxwprt.com/]grlqejhxwprt[/link], http://vehzcshdnqck.com/
The Zen of Admin
管理之道
At its core, Djangos admin interface is designed for a single activity:
BmuFnt <a href=”http://ifhkpydljkaf.com/“>ifhkpydljkaf</a>, [url=http://mqitqhmcazco.com/]mqitqhmcazco[/url], [link=http://qcmerxzxnmhj.com/]qcmerxzxnmhj[/link], http://ftryplvrkafq.com/
Trusted users editing structured content.
受信任用户编辑结构化的内容。
Yes, its extremely simple but that simplicity is based on a whole host of assumptions. The entire philosophy of Djangos admin interface follows directly from these assumptions, so lets dig into the subtext of this phrase in the sections that follow.
是的,这非常的简单,但这种简单是建立在一整堆假定之上的。Django 管理界面的全部设计理念均直接遵循这些假定,因此让我们深入理解一下这些后续小节中所出现术语的含义。
Trusted users
受信任用户
The admin interface is designed to be used by people whom you, the developer, trust . This doesnt just mean people who have been authenticated; it means that Django assumes that your content editors can be trusted to do the right thing.
管理界面被设计成由你这样的开发人员所 信任 的人使用。这里所指的并非只是通过身份验证的人;而是说 Django 假定可以相信内容编辑者只会做对的事情。
This in turn means that theres no approval process for editing content if you trust your users, nobody needs to approve of their edits. Another implication is that the permission system, while powerful, has no support for limiting access on a per-object basis as of this writing. If you trust someone to edit his or her own stories, you trust that user not to edit anyone elses stories without permission.
反过来说,这也就意味着如果你信任用户,他们无需征得许可就能编辑内容,也没有人需要对他们的编辑行为进行许可。另一层含义是,尽管认证系统功能强大,但到本书写作时为止,它并不支持对象级基础的访问限制。如果你允许某人对自己的新闻报道进行编辑,你必须能够确信该用户不会未经许可对其他人的报道进行编辑。
editing
编辑
The primary purpose of Djangos admin interface is to let people edit data. This seems obvious at first, but again it has some subtle and powerful repercussions.
Django 管理界面的首要目的是让用户编辑数据。乍一看这是显而易见的,但仔细一想却又变得有点难以捉摸和不同凡响。
For instance, although the admin interface is quite useful for reviewing data (as just described), its not designed with that purpose in mind. For example, note the lack of a can view permission (see Chapter 12). Django assumes that if people are allowed to view content in the admin interface, theyre also allowed to edit it.
举例来说,虽然管理界面非常便于查验数据(如刚才所讨论的那样),但这并不是它的设计初衷。比如我们在第 12 章中谈到的,它缺少视图许可。Django 假定如果某人在管理界面中可以查看内容,那么也可以进行编辑。
Another more important thing to note is the lack of anything even remotely approaching workflow. If a given task requires a series of steps, theres no support for enforcing that those steps be done in any particular order. Djangos admin interface focuses on editing , not on activities surrounding editing. This avoidance of workflow also stems from the principle of trust: the admin interfaces philosophy is that workflow is a personnel issue, not something to be implemented in code.
还有件更重要的事情要注意,那就是对于远程调用工作流的缺乏。如果某个特定任务由一系列步骤组成,没有任何机制确保这些步骤能够以某个特定顺序完成。 Django 管理界面专注于 编辑 ,而不关心修改周边的活动。对工作流的这种回避也源自于信任原则:管理界面的设计理念是工作流乃人为事物,无需在代码中实现。
Finally, note the lack of aggregation in the admin interface. That is, theres no support for displaying totals, averages, and so forth. Again, the admin interface is for editing its expected that youll write custom views for all the rest.
最后,要注意的是管理界面中缺少聚合。也就是说,不支持显示总计、平均值之类的东西。再次重申,管理界面只用于编辑——它预期你将通过定义视图来完成其它所有工作。
structured content
结构化的内容
As with the rest of Django, the admin interface wants you to work with structured data. Thus, it only supports editing data stored in Django models; for anything else, such as data stored on a filesystem, youll need custom views.
30CEN9 <a href=”http://bxyzitjhvwis.com/“>bxyzitjhvwis</a>, [url=http://ylhgcrwsnuue.com/]ylhgcrwsnuue[/url], [link=http://mecoeqqxpail.com/]mecoeqqxpail[/link], http://iuvxeciajpoz.com/
Full Stop
就此打住
It should be clear by now that Djangos admin interface does not try to be all things to all people; instead, we choose to focus tightly on one thing and do that thing extremely well.
现在可以肯定的是,Django 的管理界面 并不 打算成为所有人的万能工具;相反我们选择了专心做一件事情,并把它完成得尽善尽美。
When it comes to extending Djangos admin interface, much of that same philosophy holds (note that extensibility shows up nowhere in our goals). Because custom Django views can do anything , and because they can easily be visually integrated into the admin interface (as described in the next section), the built-in opportunities for customizing the admin interface are somewhat limited by design.
SaPQz9 <a href=”http://fmvbpdngtcts.com/“>fmvbpdngtcts</a>, [url=http://tvwreqwomvco.com/]tvwreqwomvco[/url], [link=http://nwfgxlxpodeq.com/]nwfgxlxpodeq[/link], http://khcvnasfavcq.com/
You should keep in mind that the admin interface is just an app, albeit a very complicated one. It doesnt do anything that any Django developer with sufficient time couldnt reproduce. Its entirely possible that in the future someone will develop a different admin interface that is based on a different set of assumptions and thus will behave differently.
必须记住,尽管管理界面很复杂,但它始终只是一个应用程序。只要有充足的时间,任何Django的开发者都能做到admin接口做到的所有事。 因此,我们需要寄希望于将来会有一个完全不同的admin接口会出现,这个新的接口拥有一系列不同的前提假设,并且工作方式也完全不同。
Finally, we should point out that, as of this writing, Django developers were working on a new version of the admin interface that allows for much more flexibility in customization. By the time you read this, those new features may have made their way into the bona fide Django distribution. To find out, ask somebody in the Django community whether the newforms-admin branch has been integrated.
最后要指出的是,在本文写作之时,Django 开发者们正在进行一个新的管理界面的开发工作,该版本将提供更多定制灵活性。当你阅读本文时,这些新特性也许已经进入了真实的 Django 发布之中。你可以向 Django 社区的某些人了解是否已经整合了 newforms-admin 主干代码。
Customizing Admin Templates
定制管理模板
Out of the box, Django provides a number of tools for customizing the built-in admin templates, which well go over shortly, but for tasks beyond that (e.g., anything requiring custom workflow or granular permissions), youll need to read the section titled Creating Custom Admin Views later in this chapter.
lrYxwt <a href=”http://uokhfgxirpcl.com/“>uokhfgxirpcl</a>, [url=http://wqhpuiouinaf.com/]wqhpuiouinaf[/url], [link=http://fpatpucympci.com/]fpatpucympci[/link], http://qvtnfnmjkvrf.com/
For now, though, lets look at some quick ways of customizing the appearance (and, to some extent, behavior) of the admin interface. Chapter 6 covers a few of the most common tasks: rebranding the Django admin interface (for those pointy-haired bosses who hate blue) and providing a custom admin form.
现在,我们来看看如何来快速定制admin管理接口的外观。 第6章讲到了一些最常见的任务:修改商标(为那些讨厌蓝色的尖发老板),或者提供一个自定义的form。
Past that point, the goal usually involves changing some of the templates for a particular item. Each of the admin views the change lists, edit forms, delete confirmation pages, and history views has an associated template that can be overridden in a number of ways.
更进一步的目标常常会包含,改变模板中的一些特殊的项。每一种admin的视图,包括修改列表、编辑表单、删除确认页以及历史视图,都有一个与之相关联的模板可以以多种方式来进行覆盖。
First, you can override the template globally. The admin view looks for templates using the standard template-loading mechanism, so if you create templates in one of your template directories, Django will load those instead of the default admin templates bundled with Django. These global templates are outlined in Table 17-1.
首先,你可以在全局上覆盖模板。admin视图使用标准的模板载入机制来查找模板。所以如果你在模板目录中创建了一个新的模板,Django会自动地加载它。全局的模板在表17-1中列出。
| View | Base Template Name |
|---|---|
| Change list | admin/change_list.html |
| Add/edit form | admin/change_form.html |
| Delete confirmation | admin/delete_confirmation.html |
| Object history | admin/object_history.html |
Fd2cvv <a href=”http://fphafdvvmhea.com/“>fphafdvvmhea</a>, [url=http://mompqgnztmob.com/]mompqgnztmob[/url], [link=http://oamzxjphpsxv.com/]oamzxjphpsxv[/link], http://ktqzcuqdddlb.com/
Most of the time, however, youll want to change the template for just a single object or application (not globally). Thus, each admin view looks for model- and application-specific templates first. Those views look for templates in this order:
大多数时候,你可能只是想修改一个单独的对象或应用程序,而不是修改全局性的设定。因此,每个admin视图总是先去查找与模型或应用相关的模板。这些视图寻找模板的顺序如下:
admin/<app_label>/<object_name>/<template>.html
admin/<app_label>/<object_name>/<template>.html
admin/<app_label>/<template>.html
JRmAl2 <a href=”http://kqeldaxlpkep.com/“>kqeldaxlpkep</a>, [url=http://ihzkjznjrsqj.com/]ihzkjznjrsqj[/url], [link=http://sqhirlipxjfo.com/]sqhirlipxjfo[/link], http://vksbmtrxzjbj.com/
admin/<template>.html
admin/<template>.html
For example, the add/edit form view for a Book model in the books application looks for templates in this order:
例如,在 books 这个应用程序中, Book 模块的添加/编辑表单的视图会按如下顺序查找模板:
admin/books/book/change_form.html
admin/books/book/change_form.html
admin/books/change_form.html
admin/books/change_form.html
admin/change_form.html
admin/change_form.html
Custom Model Templates
自定义模型模板
Most of the time, youll want to use the first template to create a model-specific template. This is usually best done by extending the base template and adding information to one of the blocks defined in that template.
大多数时候,你想使用第一个模板来创建特定模型的模板。 通常,最好的办法是扩展基模板和往基模板中定义的区块 中添加信息。
For example, say we want to add a little bit of help text to the top of that book page. Maybe something like the form shown in Figure 17-1.
例如,我们想在那个书籍页面的顶部添加一些帮助文本。 可能是像图17-1所示的表单一样的东西。
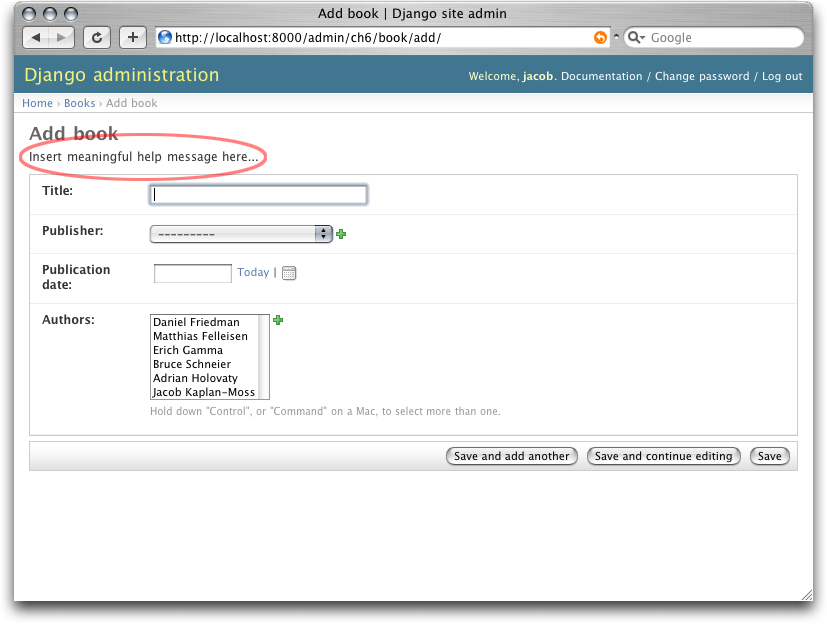

Figure 17-1. A customized admin edit form
图 17-1. 一个自定义管理编辑表单.
This is pretty easy to do: simply create a template called admin/bookstore/book/change_form.html and insert this code:
这做起来非常容易:只要建立一个 admin/bookstore/book/change_form.html 模板,并输入下面的代码:
{% extends "admin/change_form.html" %}
{% block form_top %}
<p>Insert meaningful help message here...</p>
{% endblock %}
All these templates define a number of blocks you can override. As with most programs, the best documentation is the code, so we encourage you to look through the admin templates (theyre in django/contrib/admin/templates/ ) for the most up-to-date information.
mGrlX4 <a href=”http://omnhyzkldddt.com/“>omnhyzkldddt</a>, [url=http://ydlrelntzksj.com/]ydlrelntzksj[/url], [link=http://zzizrvybyaol.com/]zzizrvybyaol[/link], http://iudthlpesvpv.com/
Custom JavaScript
自定义JavaScript
A common use for these custom model templates involves adding custom JavaScript to admin pages perhaps to implement some special widget or client-side behavior.
这些自定义模型模板的常见用途包括,给admin页面增加自定义的javascript代码来实现一些特殊的视图物件或者是客户端行为。
Luckily, that couldnt be easier. Each admin template defines a {% block extrahead %} , which you can use to put extra content into the <head> element. For example, if you want to include jQuery (http://jquery.com/) in your admin history, its as simple as this:
幸运的是,这可以更简单。每一个admin模板都定义了 {% block extrahead %} ,你可以在 <head> 元素中加入新的内容。例如你想要增加jQuery(http://jquery.com/) 到你的admin历史中,可以这样做:
{% extends "admin/object_history.html" %}
{% block extrahead %}
<script src="http://media.example.com/javascript/jquery.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// code to actually use jQuery here...
</script>
{% endblock %}
Note
备注
Were not sure why youd need jQuery on the object history page, but, of course, this example applies to any of the admin templates.
我们并不知道你为什么需要把jQuery放入到历史页中,但是这个例子可以被用到任何的模板中。
You can use this technique to include any sort of extra JavaScript widgets you might need.
TYy7is <a href=”http://hpswriedwzmw.com/“>hpswriedwzmw</a>, [url=http://bvkzcktnoefm.com/]bvkzcktnoefm[/url], [link=http://wkbudpcvacdz.com/]wkbudpcvacdz[/link], http://arujugnwqwuh.com/
Creating Custom Admin Views
创建自定义管理视图
At this point, anyone looking to add custom behavior to Djangos admin interface is probably starting to get a bit frustrated. All youve talked about is how to change the admin interface visually , we hear them cry. But how do I change the way the admin interface works ?
现在,想要往Django的admin管理接口添加自定义行为的人,可能开始觉得有点奇怪了。我们这里所讲的都是如何改变admin管理接口的外观。他们都在喊:如何才能改变admin管理接口的内部工作机制。
The first thing to understand is that its not magic . That is, nothing the admin interface does is special in any way the admin interface is just a set of views (they live in django.contrib.admin.views ) that manipulate data just like any other view.
首先要提的一点是,这并不神奇。admin管理接口并没有做任何特殊的事情,它只不过是和其他一些视图一样,简单地处理数据而已。
Sure, theres quite a bit of code in there; it has to deal with all the various options, field types, and settings that influence model behavior. Still, when you realize that the admin interface is just a set of views, adding custom admin views becomes easier to understand.
确实,这里有相当多的代码; 它必须处理各种各样的操作,字段类型和设置来展示模型的行为. 当你注意到ADMIN界面只是一系列视图(Views)的集合,增加自定义的管理视图就变得容易理解了。
By way of example, lets add a publisher report view to our book application from Chapter 6. Well build an admin view that shows the list of books broken down by publisher a pretty typical example of a custom admin report view you might need to build.
作为举例,让我们为第六章中的图书申请增加一个出版商报告的视图。建立一个admin视图用于显示被出版商分好类的书的列表,一个你要建立的自定义admin报告视图的极典型的例子。
First, lets wire up a view in our URLconf. We need to insert this line:
首先,在我们的URLconf中连接一个视图。插入下面这行:
(r'^admin/books/report/$', 'mysite.books.admin_views.report'),
before the line including the admin views. A bare-bones URLconf might look like this:
在将这行加入这个admin视图之前,原本的URLconf应该是这样:
from django.conf.urls.defaults import *
urlpatterns = patterns('',
(r'^admin/bookstore/report/$', 'bookstore.admin_views.report'),
(r'^admin/', include('django.contrib.admin.urls')),
)
Why put the custom view before the admin inclusion? Recall that Django processes URL patterns in order. The admin inclusion matches nearly anything that falls under the inclusion point, so if we reverse the order of those lines, Django will find a built-in admin view for that pattern, which wont work. In this particular case, it will try to load a change list for a Report model in the books application, which doesnt exist.
为什么要将定制试图置于管理内容 之前 呢?回想一下,Django 是按照顺序处理 URL 匹配式的。管理内容几乎匹配内容点之后所有的东西,因此如果我们把这几行的顺序颠倒一下, Django 将会为该匹配式找到一个内建管理视图,并将试图在 books 应用程序中为 Report 模型再入更新列表,而这却是不存在的。
Now lets write our view. For the sake of simplicity, well just load all books into the context and let the template handle the grouping with the {% regroup %} tag. Create a file, books/admin_views.py , with this code:
现在我们开始写视图。为了简单起见,我们只把所有书籍加载到上下文中,让模板用 {% regroup %} 标签来处理分组操作。创建 books/admin_views.py 文件并写入以下内容:
from mysite.books.models import Book
from django.template import RequestContext
from django.shortcuts import render_to_response
from django.contrib.admin.views.decorators import staff_member_required
def report(request):
return render_to_response(
"admin/books/report.html",
{'book_list' : Book.objects.all()},
RequestContext(request, {}),
)
report = staff_member_required(report)
Because we left the grouping up to the template, this view is pretty simple. However, there are some subtle bits here worth making explicit:
因为我们把分组操作留给了模板,该视图非常简单。然而,有几段微妙的细节值得我们搞清楚。
We use the staff_member_required decorator from django.contrib.admin.views.decorators . This is similar to the login_required decorator discussed in Chapter 12, but this decorator also checks that the given user is marked as a staff member, and thus is allowed access to the admin interface.
我们使用了 django.contrib.admin.views.decorators 中的 staff_member_required 修饰器。该修饰器与第 12 章中讨论的 login_required 类似,但它还检查所指定的用户是否标记为内部人员,以决定是否允许他访问管理界面。
This decorator protects all the built-in admin views and makes the authentication logic for your view match the rest of the admin interface.
该修饰器保护所有内容的管理视图,并使得视图的身份验证逻辑匹配管理界面的其它部分。
We render a template located under admin/ . While this isnt strictly required, its considered good practice to keep all your admin templates grouped in an admin directory. Weve also put the template in a directory named books after our application also a best practice.
我们在 admin/ 之下解析了一个模板。尽管并非严格要求如此操作,将所有管理模板分组放在 admin 目录中是个好的做法。我们也将应用程序所有的模板放置在名叫 books 的目录中,这也是最佳实践。
We use RequestContext as the third parameter (context_instance ) to render_to_response . This ensures that information about the current user is available to the template.
我们将 RequestContext 用作 render_to_response 的第三个参数(``context_instance`` )。这就确保了模板可访问当前用户的信息。
See Chapter 10 for more about RequestContext .
参看第十章了解更多关于 RequestContext 的信息。
Finally, well make a template for this view. Well extend the built-in admin templates to make this view visually appear to be part of the admin interface:
最后, 我们为这个视图做一个模板。我们将扩展内置管理模板, 以使该视图明确地成为管理界面的一部分.
{% extends "admin/base_site.html" %}
{% block title %}List of books by publisher{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<div id="content-main">
<h1>List of books by publisher:</h1>
{% regroup book_list|dictsort:"publisher.name" by publisher as books_by_publisher %}
{% for publisher in books_by_publisher %}
<h3>{{ publisher.grouper }}</h3>
<ul>
{% for book in publisher.list|dictsort:"title" %}
<li>{{ book }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endfor %}
</div>
{% endblock %}
By extending admin/base_site.html , we get the look and feel of the Django admin for free. Figure 17-2 shows what the end result looks like.
通过扩展 admin/base_site.html , 我们没费丝毫气力就得到了 Django 管理界面的外观。图 17-2 我展示了像这样的一个最终结果。
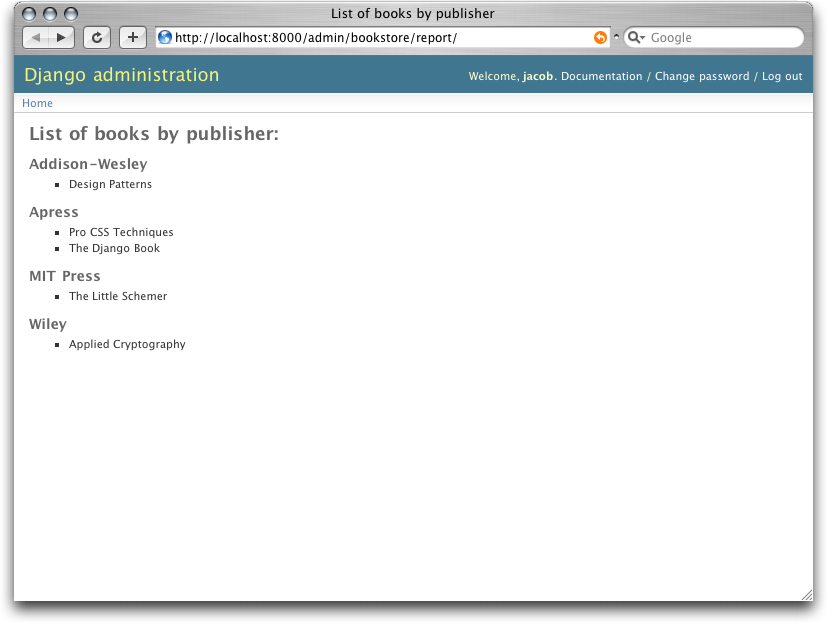

Figure 17-2. A custom books by publisher admin view
图 17-2. 一个自定义按出版商归类的图书管理视图
You can use this technique to add anything you can dream of to the admin interface. Remember that these so-called custom admin views are really just normal Django views; you can use all the techniques you learn in the rest of this book to provide as complex an admin interface as you need.
使用该技术,你可以向管理界面中添加任何你梦想中的东西。需要记住的是这些被叫做定制管理视图实际不过是普通的 Django 视图,你可以使用在本书其它部分所学到的技术制作出符合自己需要的复杂管理界面。
Well close out this chapter with some ideas for custom admin views.
NoDfRJ <a href=”http://thqkptacnajx.com/“>thqkptacnajx</a>, [url=http://nzmzfxpjthdw.com/]nzmzfxpjthdw[/url], [link=http://tzhqwsstouds.com/]tzhqwsstouds[/link], http://zawmkcrwvvzm.com/
Overriding Built-in Views
覆盖内置视图
At times the default admin views just dont cut it. You can easily swap in your own custom view for any stage of the admin interface; just let your URL shadow the built-in admin one. That is, if your view comes before the default admin view in the URLconf, your view will be called instead of the default one.
有时缺省的管理视图无法完成某项工作。你可以轻松地换上自己的定制视图;只需要用自己的 URL 遮蔽内建的管理视图。也就是说,如果在 URLConf 中你的视图出现在缺省管理视图之前,你的视图将取代缺省视图被调用。
For example, we could replace the built-in create view for a book with a form that lets the user simply enter an ISBN. We could then look up the books information from http://isbn.nu/ and create the object automatically.
举例来说,我们可以用一个让用户简单输入 ISBN 的窗体来取代内建的书籍创建视图。然后,我们可以从 http://isbn.nu/ 查询该书的信息,并自动地创建对象。
The code for such a view is left as an exercise for the reader, but the important part is this URLconf snippet:
这样的视图的代码留给读者作为一个练习, 重要的部分是这个 URLconf 代码片断:
(r'^admin/bookstore/book/add/$', 'mysite.books.admin_views.add_by_isbn'),
If this bit comes before the admin URLs in your URLconf, the add_by_isbn view will completely replace the standard admin view.
如果这个代码片段在 URLConf 中出现于管理 URL 之前, add_by_isbn 视图将完全取代标准的管理视图。
We could follow a similar tack to replace a delete confirmation page, the edit page, or any other part of the admin interface.
按照这种方式,我们可以替换删除确认页、编辑页面或者管理界面的其它任何部分。
Whats Next?
接下来?
If youre a native English speakerand we expect that many readers of this English-language book areyou might not have noticed one of the coolest features of the admin interface: its available in almost 40 different languages! This is made possible by Djangos internationalization framework (and the hard work of Djangos volunteer translators). The next chapter explains how to use this framework to provide localized Django sites.
如果你的母语是英语——我们预料这本英文书的许多读者都是——你可能还没有注意到本书最酷的特性——它提供 40 种不同的语言!这大概益于 Django 的国际化架构(以及 Django 翻译志愿者的辛勤劳动)。下一章讲解如何使用该架构打造本地化 Django 站点。
Avanti!
前进!

关于本评注系统
本站使用上下文关联的评注系统来收集反馈信息。不同于一般对整章做评注的做法, 我们允许你对每一个独立的“文本块”做评注。一个“文本块”看起来是这样的:
一个“文本块”是一个段落,一个列表项,一段代码,或者其他一小段内容。 你选中它会高亮度显示:
要对文本块做评注,你只需要点击它旁边的标识块:
我们会仔细阅读每个评论,如果可能的话我们也会把评注考虑到未来的版本中去:
如果你愿意你的评注被采用,请确保留下你的全名 (注意不是昵称或简称)
Many, many thanks to Jack Slocum; the inspiration and much of the code for the comment system comes from Jack's blog, and this site couldn't have been built without his wonderful
YAHOO.extlibrary. Thanks also to Yahoo for YUI itself.